Create Job Specifications
A Job is the fundamental execution unit of an Optimus data pipeline. It can be scheduled, configured and is always mapped to a single transformation type (eg, BQ-to-BQ, GCS-to-BQ, etc). It can have dependencies over other jobs and should only execute once the dependent job is successfully completed.
A job can also be configured with Hooks as part of its lifecycle, which can be triggered before or after the job. Please go through the concept to know more about it.
Before we begin, let’s understand the flow of job creation & deployment (later) in Optimus.
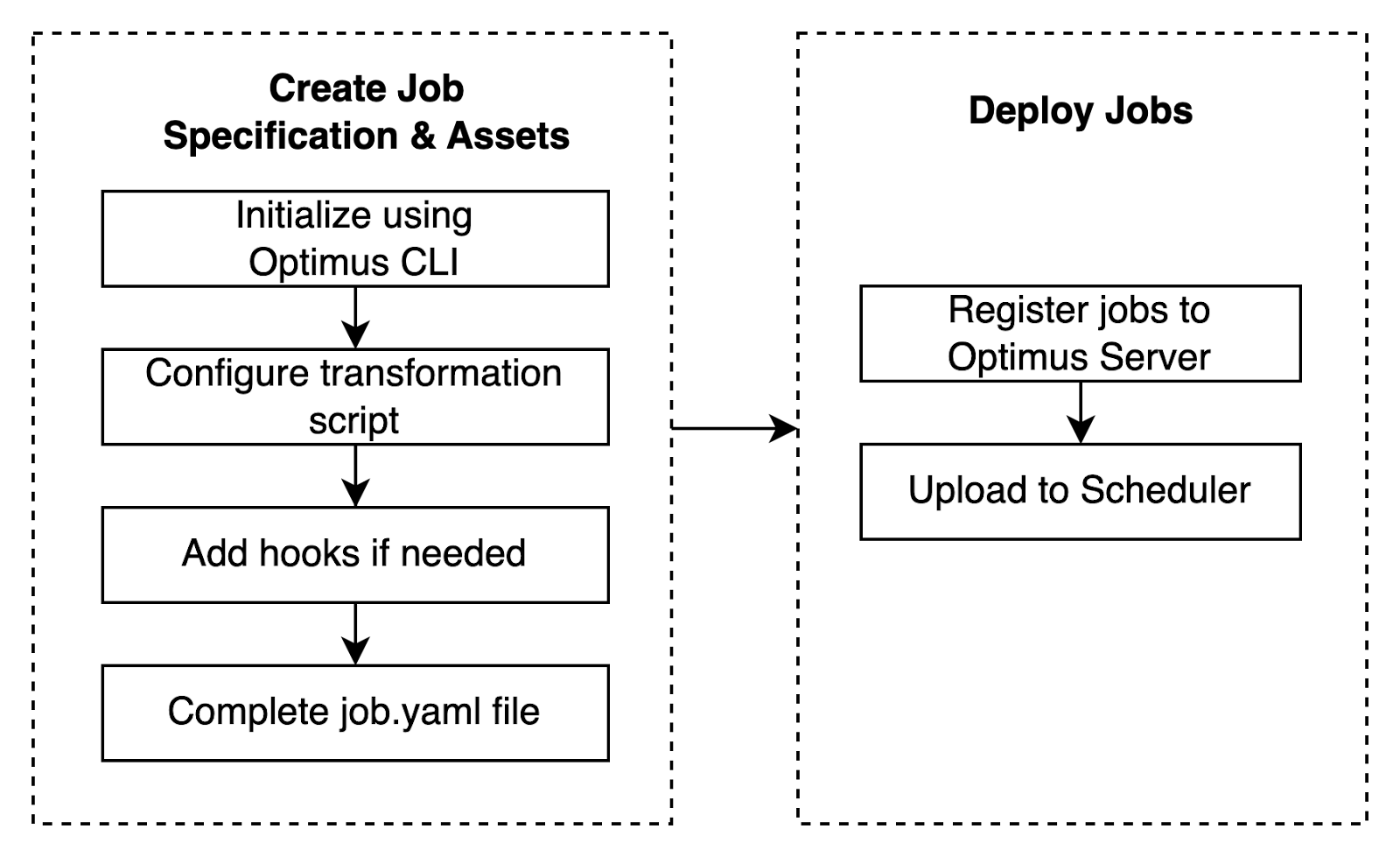
For this guide, we'll be creating a job that writes "hello YYYY-MM-DD" to a table every day at 03.00 AM. We'll use the BQ-to-BQ transformation type. For the purpose of this guide, we'll assume that the Google Cloud Project name is "sample-project" & dataset is just called "playground".
Initialize Job Specification
Open your terminal and create a new directory that will hold the specifications created by Optimus CLI. Once ready, you can run the following command and answer the corresponding prompts (do note that some prompts would be to select from options instead of input):
$ optimus job create
? Please choose the namespace: sample_namespace
? Provide new directory name to create for this spec? [.] sample-project.playground.table1
? What is the job name? sample-project.playground.table1
? Who is the owner of this job? sample_owner
? Select task to run? bq2bq
? Specify the schedule start date 2023-01-26
? Specify the schedule interval (in crontab notation) 0 2 * * *
? Transformation window daily
? Project ID sample-project
? Dataset Name playground
? Table ID table1
? Load method to use on destination REPLACE
Job successfully created at sample-project.playground.table1
After running the job create command, the job specification file and assets directory are created in the following directory.
├── sample_namespace
│ └── jobs
| └── sample-project.playground.table1
| └── assets
| └── query.sql
| └── job.yaml
│ └── resources
└── optimus.yaml
Do notice that query.sql file is also generated. This is because, for BQ to BQ job, transformation logic lies in the query.sql file. We will update this file based on the requirement later.
For now, let’s take a deeper look at the job.yaml that Optimus has generated and understands what it does. After taking a look at the possible configurations, we will try to complete the transformation task and take a look at how to add a hook.
version: 1
name: sample-project.playground.table1
owner: sample_owner
schedule:
start_date: "2023-01-26"
interval: 0 2 * * *
behavior:
depends_on_past: false
task:
name: bq2bq
config:
DATASET: playground
LOAD_METHOD: REPLACE
PROJECT: sample-project
SQL_TYPE: STANDARD
TABLE: table1
window:
size: 24h
offset: "0"
truncate_to: d
labels:
orchestrator: optimus
hooks: []
dependencies: []
Understanding the Job Specifications
| Job Configuration | Description |
|---|---|
| Version | Version 1 and 2 (recommended) are available. This affects the windowing capability. |
| Name | Should be unique in the project. |
| Owner | Owner of the job, can be an email, team name, slack handle, or anything that works for your team. |
| Schedule | Specifications needed to schedule a job, such as start_date, end_date and interval (cron) |
| Behavior | Specifications that represents how the scheduled jobs should behave, for example when the run is failed. |
| Task | Specifications related to the transformation task |
| Hooks | Name & configuration of pre/post hooks. Take a look at how to add hooks here. |
| Labels | Help you to identify your job. Any of the values will also be marked as a tag in Airflow. |
| Dependencies | Represent the list of jobs that are considered upstream. |
| Metadata | Represents additional resource and scheduler configurations. |
Behavior
Behavior specification might consist:
- depends_on_past: set to true to not allow the task to run, if the previous task run has not been succeeded yet
- retry
- count: represents how many times it will try to retrigger the job if the job failed to run
- delay
- exponential_backoff
- notify: Alert configurations. Take a look more at this here.
Task
Task specification might consist:
- name
- config: Some configs might be needed for a specific task type. For example, for BQ to BQ task, it is required to have BQ_SERVICE_ACCOUNT, PROJECT, DATASET, TABLE, SQL_TYPE, LOAD_METHOD configs. Take a look at the details of what is load method here.
- window: Take a look at the details of the window here.
Dependencies
Represent the list of jobs that are considered upstream.
- If the job is in a different project, include the Optimus’ project name in the prefix.
- If the job is in the same project, simply mentioning the job name is sufficient.
Example:
dependencies:
- job: sample-project.playground.table1
- job: other-project/other-project.playground.table2
Metadata
Below specifications can be set in Metadata section:
- resource: set up CPU/memory request/limit
- airflow: set up which Airflow pool and what is the queue configuration for this job
Completing the Transformation Task
Let’s retake a look at the generated task specifications
task:
name: bq2bq
config:
DATASET: playground
LOAD_METHOD: REPLACE
PROJECT: sample-project
SQL_TYPE: STANDARD
TABLE: table1
window:
size: 24h
offset: "0"
truncate_to: d
Here are the details of each configuration and the allowed values:
| Config Name | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|
| PROJECT | GCP project ID of the destination BigQuery table | |
| DATASET | BigQuery dataset name of the destination table | |
| TABLE | the table name of the destination table | |
| LOAD_METHOD | method to load data to the destination tables | Take a detailed look here |
| PARTITION_FILTER | Used to identify target partitions to replace in a REPLACE query. This can be left empty and Optimus will figure out the target partitions automatically but it's cheaper and faster to specify the condition. This filter will be used as a where clause in a merge statement to delete the partitions from the destination table. | event_timestamp >= "{{.DSTART}}" AND event_timestamp < "{{.DEND}}" |
Now let's try to modify the core transformation logic that lies in assets/query.sql. Remember that we are going to
create a job that writes "hello YYYY-MM-DD" to a table every day at 03.00 AM. Now, let’s modify the query so it prints
what we intended:
SELECT CONCAT("Hello, ", "{{.DEND}}") AS message;
{{.DEND}} is a macro that is replaced with the current execution date (in YYYY-MM-DD format) of the task ( note that this is the execution date of when the task was supposed to run, not when it actually runs). Take a detailed look at the supported macros here.
Do notice that the query is not sourcing from any other table. This means the job we are creating will not have any
dependency unless we manually specify so in the job specification YAML file.
However, if for any reason you are querying from another resource and want to ignore the dependency, add
@ignoreupstream annotation just before the table name, for example:
SELECT column1, column2, column3
FROM `sample-project.playground.source1` s1
LEFT JOIN /* @ignoreupstream */
`sample-project.playground.source2` s2
ON (s1.id = s2.s1_id)
WHERE
DATE(`load_timestamp`) >= DATE('{{.DSTART}}')
AND DATE(`load_timestamp`) < DATE('{{.DEND}}');
Adding Hook
There might be a certain operation that you might want to run before or after the Job. Please go through the concept to know more about it.
For this guide, let’s add a post hook that will audit our BigQuery data using Predator. You can find the Predator plugin YAML file here and have the plugin installed in your server and client.
In order to add a hook to an existing Job, run the following command and answer the corresponding prompts:
$ optimus job addhook
? Please choose the namespace: sample_namespace
? Select a Job sample-project.playground.table1
? Filter expression for extracting transformation rows? __PARTITION__ >= date("{{ .DSTART | Date }}") AND __PARTITION__ < date("{{ .DEND | Date }}")
? Specify the profile/audit result grouping field (empty to not group the result)
? Choose the profiling mode complete
Hook successfully added to sample-project.playground.table1
With the above prompt, we're adding the predator hook post the execution of the primary job. Filter expression configuration and the rest of the questions are specific to a predator hook, and it might be different for other hooks.
After this, existing job.yaml file will get updated with the new hook config.
hooks:
- name: predator
config:
AUDIT_TIME: "{{.EXECUTION_TIME}}"
BQ_DATASET: "{{.TASK__DATASET}}"
BQ_PROJECT: "{{.TASK__PROJECT}}"
BQ_TABLE: "{{.TASK__TABLE}}"
FILTER: __PARTITION__ >= date("{{ .DSTART | Date }}") AND __PARTITION__ < date("{{ .DEND | Date }}")
GROUP: ""
MODE: complete
PREDATOR_URL: "{{.GLOBAL__PREDATOR_HOST}}"
SUB_COMMAND: profile_audit